Bloom’s taxonomy is a constructive framework for teaching, learning and earning educational accomplishment; the educators identify and discover the academic level at which the students are comfortable and capable of learning. Bloom’s taxonomy devises a hierarchical system of education that aims at developing abilities, cognitive skills, etc. The main elements of Bloom’s taxonomy focus on the evaluation, analysis, knowledge and much more. In addition, it aims at brimming the students with the utmost understanding, i.e., from teaching them about basic facts to let them gain an extensive understanding of various subjects. Bloom’s taxonomy facilitates a step by step process of learning. Hence, each level or step of this pedagogical process is an essential part of education.
Teachers play a vital role in uplifting Bloom’s taxonomy by introducing activities for students like assignments, assessments to support the crucial objectives involved in each level of the learning process.
Bloom’s taxonomy is an aggregation of crucial objectives such as Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor. The aim of understanding these objectives is to equip the learner with knowledge, skills and attitude towards a particular subject.
How is OBE related to Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Outcome-based education is one of the educational systems that focus on achieving outcomes. The educational institutions introduce curricula, assessments and instruction based on expected objectives and enable the students to demonstrate learning outcomes at the end of the program. Bloom’s taxonomy identifies and discovers the realms of learning like Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor. In addition, bloom’s taxonomy is one of the powerful tools that define the Objectives. It allows you to understand the concept, Analyze the same and then Evaluate them. Bloom’s education lays the foundation of learning and enables you to Understand those objectives and master them towards the end of the program.
What are the important objectives in Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s taxonomy is an aggregation of crucial objectives such as Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor. The aim of understanding these objectives is to equip the learner with knowledge, skills and attitude towards a particular subject.
Cognitive
Within the cognitive domain in Bloom’s taxonomy, equipping oneself with knowledge and skills is an important aspect, whereby a student can learn to identify and acknowledge various concepts that would serve as the basis of the learning process. Here, you get to recall the crucial facets of Bloom’s taxonomy, which are analysis, comprehension, knowledge and evaluation.
Affective
In the affective domain in Bloom’s taxonomy, a student gets to imbibe new values, attitudes and emotions towards a particular subject. They reflect and exhibit positive signs like being a good listener, staying receptive, patient, empathetic etc. With this, they focus on applying their knowledge in a real world scenario and are assessed on the same. Yet, such attitudes reflect internalized virtues.
Psychomotor
In the psychomotor domain, the learners get to develop motor skills like coordination and manual tasks. For instance, psychomotor skills can range from operating complex machinery to teaching students as well as participating in activities like yoga. Such things are measured and evaluated on various factors like technique, the procedure involved and speed.
What are the different levels of Bloom’s taxonomy?
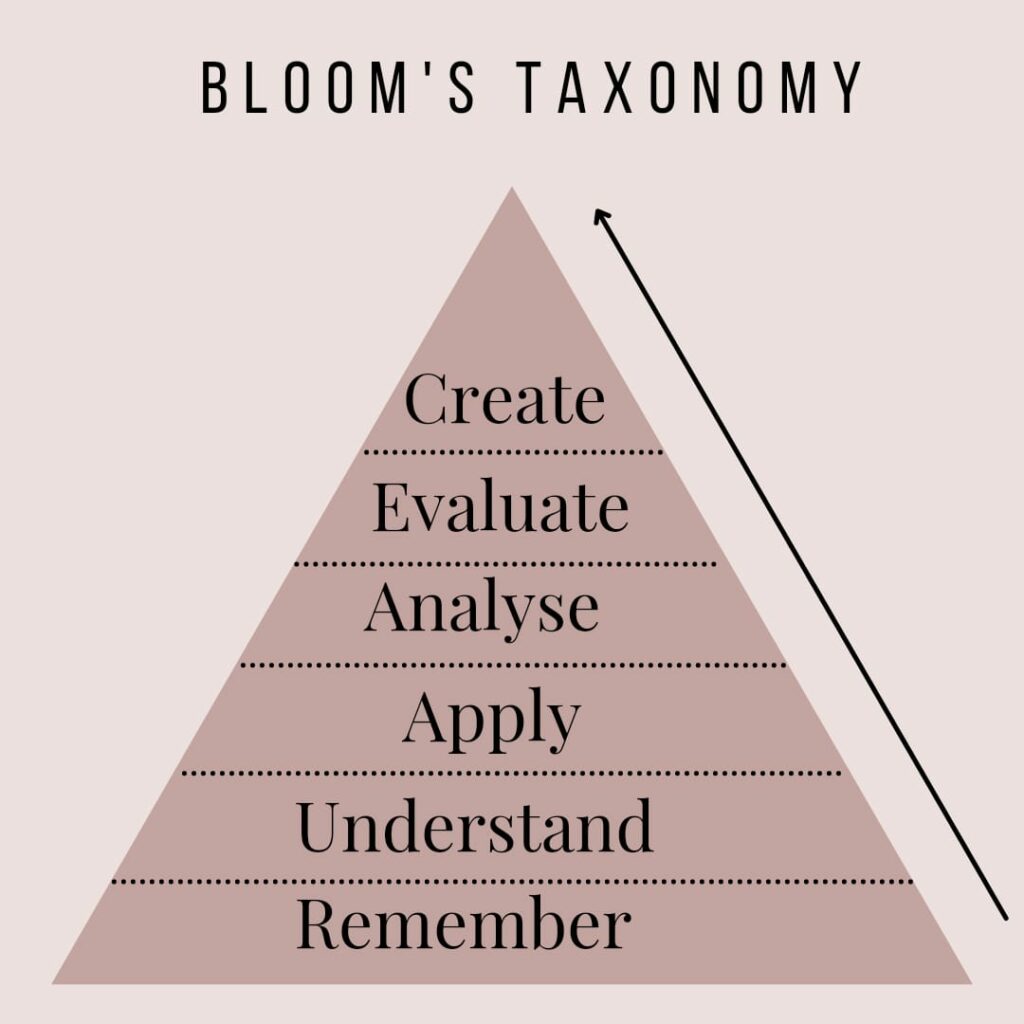
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a gradual process where each factor or facet of this learning model is followed and well taken care of. The level of thinking is given a hierarchical structure that encourages and stimulates the individuals to start from achieving small goals and then mastering the higher objectives. In total, this level of thinking is designed in a pyramid framework where one is accustomed to achieving the goals from the bottom level and working upwards to accomplishing the higher-level goals.
The lower level objectives lay a foundation for your learning process and have to be mastered before moving up the ladder (to achieve higher goals). Meanwhile, the higher-level objectives aim at providing in-depth learning with a greater degree of cognitive understanding, which, probably, can be accomplished once the lower level goals are achieved.
In simple words, students are expected to attain all the levels of Bloom’s taxonomy, while measuring their progress towards the learning process. Let’s understand the different levels of learning involved in bloom’s taxonomy.
Remembering
In this level of learning, educators introduce a question and answer round while letting the students memorize, recall and reflect upon what they remember about lectures, stories, etc. The point is it shows how the students are using their cognitive skills in an effective learning process.
In addition, this is a basic level of learning, yet the most crucial one. It builds a rock-solid foundation that helps the students achieve complex objectives in the long run. Hence, at this stage of learning, students are supposed to recall, rethink and remember the facts.
Understanding
In the second stage of Bloom’s taxonomy, students are supposed to remember, reflect and explain the concept from their perspective. Once they understand the plot of a story, they will have to summarize or articulate the same from their level of perception. While doing so, the students will be able to put forward various analogies or explanations. Hence, it is vital to understand, assess and then comprehend concepts while explaining them from one’s viewpoint. This way, the students will be able to work on evaluating their skills of interpretation.
Applying
It is the third level of bloom’s taxonomy, where students are expected to apply theoretical knowledge to practical experiences. It is all about grasping the learned concepts and correlating them outside the domains of the classroom. In addition, the third factor focuses on demonstrating, applying and understanding to real-world problems. In this way, students can apply their knowledge and learn from actual experiences.
Analyzing
As we move up the ladder in reaching the higher objectives of Bloom’s taxonomy, students can rationally think, understand and interpret the situations well. They use their cognitive skills to speculate and differentiate between various concepts while understanding the reasoning behind them. Furthermore, the learners at this stage aim to examine and inspect anything that catches their attention to try and understand the same. Yet, here, the students mainly focus on ‘how’ and ‘why’.
Evaluating
In the fifth stage of Bloom’s taxonomy, the learners form an opinion/ judgment about any concept they have examined. They turn receptive and focus on rendering solutions, suggestions or possibilities about anything that excites them. This way, the students become aware and observant in their patterns of thinking. Hence, they evaluate the judgments and put forward their understanding of a situation with a reasonable explanation.
Creating
In the final stage of Bloom’s taxonomy, the learner is expected to exemplify their knowledge; they apply whatever they have understood while creating something from the learning experience. For instance, it can be forming a thesis, writing an essay, a report, etc. The point is, your gained knowledge should be demonstrated by you, either by formulating a conceptual theory or by designing something (tangible).
How does Bloom’s taxonomy impact education?
Education is a prerequisite to the development of the individual’s attitude, thinking and cognitive abilities. Similarly, bloom’s education is one of the best models of learning that imparts valuable knowledge and skills to the learners. In addition, it allows teachers to make reasonable decisions while ensuring convenience for the students. Such learning supports and instils high order thinking for helping students adapt critical thinking skills. It allows the educators to formulate the curriculum based on bloom’s taxonomy.
Moreover, a tutor can focus on forming projects/activities that will shape students’ thought process, knowledge and understanding. Hence, it is a constructive mode of learning.
How do we analyze students using Bloom’s education?
Initially, the students are introduced to the concept of bloom’s taxonomy. Once the educator talks about such a concept, they ask the learners to devise various questions based on each level involved in taxonomy. This way, the teachers guide them with answers and show them how it is done. Subsequently, upon explaining this, teachers arrive at the actual level of implementation. For instance, after teaching the students about the topic of Electric current, she can go through the six questions for each level with the learners. Together, the students can learn to form answers which will help them know the things expected from them.
The educators prepare the students for assessment to evaluate whatever they have learned from the lessons taught. While formulating the assessment, they use abstract questions, as the learners get to think and then evaluate. One can even form insightful assessments while including MCQs, etc.
How does Bloom’s Taxonomy help teachers?
Bloom’s taxonomy is one of the best tools for teachers to help students attain cognitive skills and knowledge. In the levels of taxonomy, the educators can focus on learning objectives for the learners and formulate the work plan accordingly. The teachers focus on the students’ development and help them become rational beings while ensuring their progress for long term goals. Bloom’s taxonomy has a hierarchical system of learning that specifies the learning objectives, which helps the educators mould their lesson plan.
In addition, the teachers can leverage such method, as it is one of the most comfortable learning processes. The students tend to become comfortable with this educational setting. For instance, teachers are well-versed with the levels of thinking involved in a taxonomy; the educators can form or design their objectives while keeping in mind the levels of thinking.
Conclusion
Bloom’s taxonomy focuses on brimming the students with high order thinking skills and knowledge. Within levels of Bloom’s taxonomy, one can begin by attaining the less cognitive goals, but it does lay a strong foundation for helping the students achieve higher cognitive goals. In total, such a learning process moulds them into a rational and knowledgeable person. It even expects the students to attain all the respective attributes by the end of every assessment.

About the Author: Hansika Bhardwaj
Hansika is a proud content writer and enthusiastic person who is willing to embrace the journey. She loves writing poetry when not spending her time researching on education and education technology. She believes and manifests the ideals of hope, magic and positivity. Hansika is currently a student in Humanities Dept. at University of Delhi.
This article has been re-published on Medium





Woahhhhh veryy insightful and informative thought’s 🙌🙌💯
That’s a really deep and insightful analysis that would help the readers! Great work!
Keep going ! This helped me learning something new ♡
Informative 👍
A very informative and detailed one👏🏻